1. A ray of light is incident at 30 degrees in air on an air-glass boundary. What angle does the ray make with the normal in glass? SEE EXTENDED SOLUTION
2. A ray of light is incident at 30 degrees in water on an air-water boundary. What angle does the ray make with the normal in air?
3. A ray of light is incident at 45 degrees in glass on an air-glass boundary. What angle does the ray make with the normal in air?
4. Determine the critical angle for an air-diamond boundary? Now do the same for an air-glass boundary. Explain how the difference in these answers determines why a diamond sparkles more than a glass imitation.
5. A ray of light is incident on a slab of glass with parallel sides such that the angle of incidence theta. A) Show that regardless of the measure of the original angle of incidence, the ray emerges from the glass with the same angle theta. B) The ray of light will be shifted some distance x from its original path. Determine x in terms of theta, the index of the glass and the thickness of the glass.
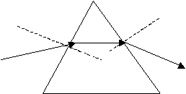
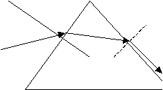
6. A ray of light is incident on a prism of glass that is cut as an equilateral triangle.
A) For what angle of incidence will the ray traverse the glass symmetrically (i.e., parallel to the base of the prism)? B) For what range of angles of incidence will the ray cross through the glass but fail to emerge from the opposite side? See the applet at http://surendranath.tripod.com/Prism/Prism.html
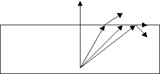
7. A stone lies at the bottom of a pool of water 1 m deep. How much of the pool surface must be covered to prevent the stone from being seen by anyone above the surface?
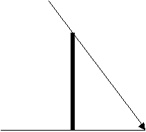
8. A meter stick is installed vertically at the bottom of a swimming pool. Light is incident on the stick at an angle of 40 degrees with the vertical. How long is the shadow cast by the stick if a) the pool is empty? b) the depth of water is 1 m? c) the depth of water is .5 m?
9. Consider a slab of glass with parallel sides. It has water on one side and air on the other. A ray of light in water is incident on the water-glass boundary at 60 degrees with the normal. What angle does the ray make with the normal as it exits the glass? Sketch a diagram of this event.
10 Consider a right angle glass prism ABC where angle B = 90 degrees and side ab is the shorter of the two legs. If a ray is incident normally on side ab, what must be the measure of the angle C such that the ray of light, upon entering the glass is reflected internally at face ac